DSP¶
This library does not provide complete DSP paths to render ADM content, but does contain some components which can be used to do so. DSP components are defined in Namespace ear::dsp.
FFT interface¶
BlockConvolver objects use a user-provided FFT implementation. These
are provided by implementing FFTImpl<float> (and therefore FFTPlan<float> and FFTWorkBuf) for the FFT library you wish to use, and
passing an instance to BlockConvolver::Context::Context().
An implementation for KISS FFT is provided by default, and may be obtained by
calling get_fft_kiss(). The implementation of this (in
src/fft_kiss.cpp) may be a useful example to show how the FFT interface
should be implemented.
Rendering DirectSpeakers¶
The gains calculated for DirectSpeakers channels using the
GainCalculatorDirectSpeakers should be applied directly to the input
audio channel to produce the output audio channels. DirectSpeakers metadata
should not be dynamic (there should be a single audioBlockFormat in each
audioChannelFormat), so gains should not be interpolated inside blocks, though
should be interpolated if metadata is changed by the user.
This may be applied using
the GainInterpolator with
LinearInterpVector.
Rendering Objects¶
The audio processing for Objects content is defined in [bs2127] section 7.1. The structure used is as in Fig. 1.
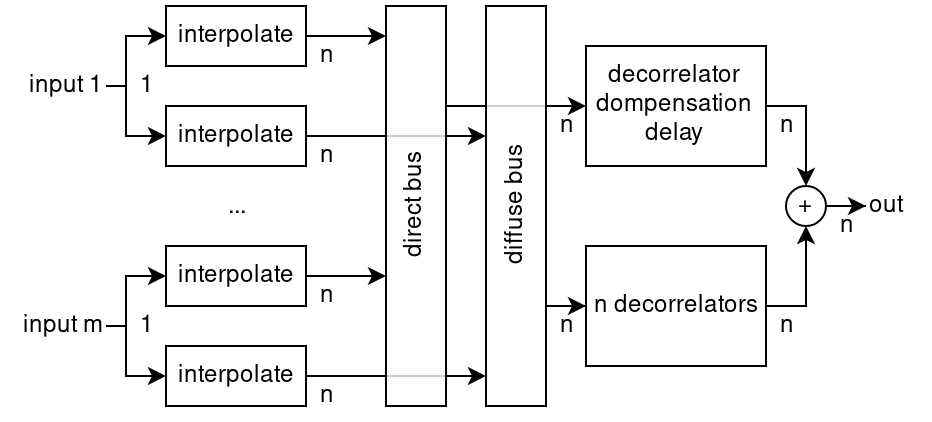
Fig. 1 Signal processing for m Objects with n output channels¶
This can be built from the following components:
GainInterpolatorwithLinearInterpVectorto interpolate and apply the gains to the incoming audio (the interp blocks in Fig. 1).DelayBuffer<float>withdecorrelatorCompensationDelay()samples delay to compensate for the decorrelator delays.BlockConvolverobjects with filters calculated usingdesignDecorrelators()to decorrelate the signals.VariableBlockSizeAdapter<float>to allow the use ofBlockConvolverobjects with variable-size sample blocks. This could be used to wrap just theBlockConvolver::process()calls, or the whole processing chain (recommended). If only the block convolvers are adapted, then the compensation delay will need to be increased byVariableBlockSizeAdapter::get_delay()samples.
Rendering HOA¶
As with DirectSpeakers, HOA metadata should not be dynamic, so the calculated matrices can be applied directly to the input audio.
The decode matrices calculated for HOA channels using the
GainCalculatorHOA should be applied directly to the input audio
channels to produce the output audio channels. As with DirectSpeakers,
HOA metadata should not be dynamic (there should be a single
audioBlockFormat in each audioChannelFormat), so gains should not be
interpolated inside blocks, though should be interpolated if metadata is
changed by the user.
This may be applied using
the GainInterpolator with
LinearInterpMatrix.